WASSCE Past Questions and Answers for Business Management 1994 is a learning resource.
This learning resource has been designed to help students to pass their exams in the above stated examining body.
I believe you are imagining what our website can offer you? If so, then just wait and see. Read more.
Click on the links below to navigate to what you specifically want. You can always click on back arrow [←] to come back to the table of content here:
Click For The Summary Of This Guide
Table of Content
General Overview
WASSCE Past Questions and Answers for Business Management 1994 is a learning resource.
This learning resource has been designed to help students to pass their exams in the above stated examining body.
I believe you are imagining what our website can offer you? If so, then just wait and see.
Also, have you had challenges trying to learn, write or pass your WAEC BM paper? If the answer is yes, then I can assure you that educareguide is here to help and guide you.
We are here to encourage you that you can easily pass this subject. Firstly, we have a lot of links to assist you to get enough details.
Truly, this will help you to gain enough knowledge and understanding to pass your examination. Secondly, we have materials on various topics, sub-topics relating to this subject area.
Therefore, our site is very helpful to Senior High School Student across the West African sub-region.
Notably, these countries are Nigeria, Ghana, Sierra Leone, The Gambia and Liberia.
Moreover, these students rely on our guide and pass the WASSCE Business Management Examination.
In detail, check the questions and the answers just below.
The Nature of the Examination
There are two Papers in the examination, (and these are Paper 1 and Paper 2). In detail, there are two sections in the Paper 1 (i.e. Section A and Section B). Section A is an Objective Test and Section B is Theory Test.
There are 50 questions in the Objective test, and there are 7 question in the theory Section.
Consequently, there are 10 questions in the Paper 2. To explain more, he question 1 is a Case Study. To explain, there are some question under the case to test the student’s understanding.
Finally, the other 9 theory questions are also theory questions. They are asked to tests the student’s general understanding of the subject are.
The Summary of the Paper
The WASSCE Business management Paper for 1994 can summarized below:
1994 WASSCE Business Management Paper One – Section A;
1994 WASSCE Business Management Paper One – Section B;
1994 WASSCE Business Management Paper Two
WASSCE Past Questions and Answers – Business Management 1994 – Paper 1
WASSCE Past Questions and Answers Bus. Management 1994 – Paper 1 – Section A
Let me show you how to find the answers to the Business Management Questions – Paper 1, Section A. To clarify that, when you read a question, just click on this symbol (˅) that follows the question.
After doing so, the answer will drop down for you. In fact, it is a very simple task.
However, for the purposes of evaluating yourself, you may want to answer the before reviewing the suggested answer (or solution)
- The training of a person to do one particular type of job or task is referred to as [expand title=””] C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- task force
- migration
- specialization
- personnel management
- Which type of business enterprise has the following features? [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
-
-
-
- No corporate existence
- Membership between 2 and 20
- Unlimited liability
- Mutual confidence and trust
-
-
-
-
-
- Partnership
- Co-operative society
- Sole proprietorship
- Limited liability company
- Business organizations have a responsibility to pay correct taxes to [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- consumers
- government
- labour unions
- investors
- A computer can best be described as a/an [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- mechanical calculator for doing work quickly
- electric tool for processing information
- photographic device for the retrieval of information
- electronic device for processing storage and retrieval of information.
- The salaries paid to government employees is classified under [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- recurrent expenditure
- capital expenditure
- balance of payments
- internal revenue
- Which of the following banks acts as a lender of last resort? [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- Merchant bank
- Commercial bank
- Central bank
- Development bank
- A contract under which one party undertakes to indemnify another against a risk is known as [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- sale of goods
- will
- partnership deed
- insurance
- Which of the following is not a document used in international trade? [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Indent
- Postal Order
- Freight note
- Bill of lading
- Which of the following best defines Balance of Payment? [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- The important of goods and services from other countries
- The exportation of goods and services from one country to the rest of the world
- The system of accounts of all transactions between one country and the rest of the world
- The method of payment for goods bought from other countries.
- Which of the following is not a function of management? [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Advertising
- Planning
- Directing
- Controlling
- All the following are conditions of a valid contract except [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- there must be an offer
- the offer must be accepted
- both parties must have legal capacity
- papers must be signed
- The process of sending information from one person to another is referred to as [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- delegation
- communication
- seminar
- meeting
- A good decision-maker must [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- write down information
- use a computer
- give order
- evaluate alternative
- Which of the following is not true of an inflationary period? [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- Goods are in short supply on the market
- The cost of production increases
- The value of money increase
- Standard of living goes down
- Tailoring, barbering and teaching are forms of [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- personal services
- constructive activities
- manufacturing
- constructional occupation
- Decision-making and control of a sole proprietorship is in the hands of [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Board of Directors
- The government
- The majority shareholder
- The individual owner
Use the chart below to answer questions 17 and 18

- Which of the following does the above chart represent? [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Function organisation
- Line and staff organization
- Information organization
- Line organisation
- The production manager in the chart will report directly to the [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Personnel Manager
- Legal Adviser
- Marketing Manager
- Managing Director
- Which of the following is responsible for the development of small-scale businesses in Ghana? [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Association of Ghana Industries
- National Board for Small Scale Industries
- Management Development and Productivity Institute
- Small Scale Business Advisory Centre
- Which of the following activities will facilitate the gathering of information for decision making in business? [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Research
- Marketing
- Production
- Quality control
- Which of the following is not a- marketing mix variable? [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- The proprietor
- The rice
- The product
- The promotion
- Acting as a store of value, money [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- enables goods to be exchanged directly
- ensures that buyers pay for the goods purchased
- prevents the deterioration of goods being stored
- facilitates the accumulation of wealth in a convenient form
- Commercial banks lend money to individuals and firms in the form of[expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Interest and dividends
- Shares and bonds
- Loans and overdrafts
- Commissions and premiums
- Which of the following do not form part of the chain of distribution? [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Wholesale businesses
- Insurance companies
- Small Scale retailers
- Forwarding and shipping agents
- Short-term financing of a business may take the form of [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Selling shares on the stock exchange
- Increasing the share capital of the firm
- Obtaining trade credit from suppliers
- Leasing plant and equipment
- When the prices of goods exported by a country fall in relation to the prices of good imported then that country. [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Has a favourable balance of payment
- Experiences favourable terms of trade
- Has an unfavourable balance of payment
- Experiences an unfavourable terms of trade
- The document which enables a consignee to clear goods from the port is [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Proforma
- Bill of lading
- Certificate of inspection
- Delivery note
- One important aim of Economic Union of nations is to [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Create a large market for member countries
- Export surplus food items to other countries
- Form a federal state with one president
- Stop importing goods from other parts of the world
- When the amount in words and figures differ on a cheque, the drawee will [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Pay the higher amount to the payee
- Ask the payee to correct the amount
- Return the cheque to the drawer
- Destroy the cheque
- Investors in business expect their investments to [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- Yield profits
- Be used to pay workers
- Get their money back without interest
- Earn interest on regular basis
- Formal communication in organization would follow [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- The line of authority
- The way employees interact
- The rules of local union
- The communication facilities available
- Which of the following is not a characteristics of private limited liability companies? [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- The owners are the shareholders of the company
- The shareholders do not have to pay the debts of the company with their personal wealth
- The shares of the company can be quoted on the Stock Exchange
- The company does not need a certificate
- Which of the following is not an advantage of specialization? [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- It makes it easy to produce on a large scale
- The goods produced are more expensive
- The cost of training workers is reduced
- It leads to lower cost of goods
- The process of changing raw materials into finished goods that consumers want is known as [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- marketing
- extraction
- specialization
- production
- All the following are extractive occupations except [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- construction
- mining
- fishing
- quarrying
- A registered company has a separate legal identity. This statement means that [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- the directors have different offices
- the company is different from its owners
- the lawyers are the owners of the company
- many people come together to form the company
- A shareholder in a limited liability company [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- will use his wealth to pay the company’s debts
- takes part in the daily activities of the company
- is responsible for appointing the Managing Director
- loses only the total value of his shares in the event of bankruptcy
- Which of the statements is not true of a co-operative society? [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- It is formed to serve the interest of members
- Each member has an equal say in managing the society
- Members have unlimited liability in case of bankruptcy
- Profits are shared according to members’ transactions with the society
- Which of the following is a bill of exchange? [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- Letter of Credit
- Cheques
- Sank Statement
- Debit note
- In a situation where an amount of money can buy a larger quantity of the same goods than before, there is said to be [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- deflation
- over production
- salary increase
- inflation
- Adam insured his brother’s house in his own name against fire and lives in the house in his brother’s absence. The house was destroyed by fire and the insurance company refused to pay any claims to him. This was because [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- fire in an uninsured risk
- the fire was not approximate cause
- Adam’s brother was not living in the house
- Adam had no insurable interest in the house.
- Under the normal product life cycle, the introduction stage is associated with [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- slow growth in sales
- peak profitability
- product imitation
- sale decline
- Which of the following is the final link in the chain of production? [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
-
- A bonded warehouses
- Manufacturing firms
- Retail businesses
- Commercial banks
- Which of the following is not an obstacle to trade between countries? [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- The legislation governing trade in the countries
- The distance between the countries
- The cultures of the countries involved
- The currencies of the countries involved
- Which of the following is not a feature of developing countries? [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- There is a high level of skilled manpower
- There is a high rate of population growth
- There is dependence on one major export crop
- There is a high level of unemployment
- Through which of the following methods will a company finance its operations on medium terms basis? [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- borrowing from friends
- discounting bills of exchange
- issuing more shares
- leasing equipment
- Which of the following is not performed by a computer? [expand title=””]C is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- It manipulates data
- It stores information
- It generates information
- It retrieves stored data
- Which of the following is not a benefit of market segmentation? [expand title=””]D is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- It enables sellers to easily recognize and compare marketing opportunity.
- Sellers are in a better position to adjust their products to suit the market.
- It gives a clear idea of markets to enable the development of appropriate marketing programmes
- Sellers are in a better position to recognise their competitors and to compete effectively.
- The main source of government revenue is [expand title=””]A is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- the taxes paid by individuals and firms
- the printing of money by the central bank.
- the sales of treasury bills and bonds to the public
- the savings of individuals and institutions
- The role of middlemen in the production of process is to [expand title=””]B is the answer -Business Management 1994 WASSCE[/expand]
- arrange for bank loans for producers
- ensure that goods reach the final consumer
- manage warehouse efficiently
- enable retailers to buy in bulk and sell in smaller quantities
WASSCE Past Questions and Answers Bus. Mgt. 1994 – Paper 1 – Section B
This section of the examination is made up of essay-type questions. That normally require you to mostly, state and explain your various points.
As I have always said, it is better to first answer the questions on your own before referring to the answer from the drop down symbol.
Let me show you how to find the answers to the Business Management Questions – Paper 1, Section B.
When you read a question, just click on this symbol (˅ )beside it, and the answer will drop down for you. It is a very simple task.
1 (a) Give five advantages of sole proprietorships over public limited liability companies in Ghana.[expand title=””]
Suggested Answer:
Advantages of sole proprietorships over public limited liability companies in Ghana
- Easy and simple formation:- It is easy and simple to start a sole proprietorship business. This is because there is no law requires you to register the business. A very small capital could be used to set it up.
- Quick decision making:- The owner has adequate control over the business. Therefore, he can take decisions alone without consulting anyone.
- Enjoyment of Privacy:- The owner can keep the records and accounts of the business as secretes since he does not account to anyone.
- With Sole proprietorship, there is close cordial relationship between the owner and his workers and customers. This is because, he deals more directly with them.
- Dedication and self-interest of owner: He takes much interest in the business in order to reduce or prevent waste. He also enjoys all the profits of the business alone.[/expand]
1 (b) State four main differences between a public limited liability company and a private limited liability company.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Whiles membership of a public limited liability company ranges from seven (7) to infinite, the membership of a private limited liability company ranges from seven (7) to fifty (50) in most cases. (Remember that, it differs in some jurisdictions).
- Public Limited Liability Company can invite the public to subscribe for shares on the stock exchange market. However, a private limited liability company is not allowed to trade on the stock exchange market.
- In private limited liability companies, shares are not transferable from one investor to another, On the other hand, public limited liability companies shares allows for easy transfer of shares among members.
- Public limited liability companies are required by law to file their annual accounts with the Registrar General’s Department. However, Private limited Liability companies are not required to do so.[/expand]
2 (a) State four possible limitations of an organizational chart.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
Limitations of an organizational chart.
- Organizational charts do not indicate the exact limits or how much authority and responsibility is attached to a particular position in an organization.
- The chart also lacks flexibility. A newly created department cannot get a place on the chart. A new chart has to be prepared which will cost the organization.
- The chart provides limited information on the complex relationships that exist in the organization. The chart does not show both formal and informal lines of communication in an organization.
- The chart implies that the organization is a static thing and this is not so considering the dynamic nature of an organization.[/expand]
2 (b) Discuss five advantages of formal organization.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- There is unity of objectives and efforts in formal organizations because all workers are operating within a framework that has been established and thus recognized.
- There is a clear hierarchy of command and control in formal organization.
- There are clear lines of communication in formal organizations, e.g., downward, upward etc.
- There is a well defined span of control and the relationship between the various departments, superior-subordinates etc.
- It is more stable and predictable because the procedures, policies and rules have already been laid down.[/expand]
3 (a) What four reasons may be given for the imposition of taxes on the citizens of a country?
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
Governments impose taxes on their citizens because of the following reasons:
- The government of a country imposes taxes on it citizens in order to raise revenue needed to administer develop the country. Taxes are needed to put up infrastructure such as roads, schools, health services, etc.
- Taxes may be imposed in order to protect vital and infant industries. In order to make local industries competitiye, the government may impose taxes. Example, tariffs imposed on imported products to discourage consumption because of high prices.
- To prevent dumping: At times governments impose taxes in order to prevent the dumping of cheap and shoddy products into the country.
- Taxes may also be imposed to redistribute income. This may be done by imposing high taxes on the rich and low taxes on the poor. This tax system is called the progressive tax system. Under progressive tax system, as a person’s income increases, the percentage paid as tax also increases.[/expand]
3 (b) Give three examples each of direct and indirect taxes.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Examples of direct taxes include:
- Personal income tax:- This is mostly imposed on individual’s income. The pay as you earn (PAYE) system operates in Ghana.
- Company tax:- Imposed on profits of limited liability companies or corporations.
- Capital gain tax:- This is a tax paid on profit received as a result of selling assets.
- Examples of indirect taxes include: –
- Excise duty:- Tax imposed on locally produced goods.
- Sales Tax:- Tax levied at the wholesale or retail level.
- Customs Duty: This is divided into import duty and export duty. Customs
duties are levied on imports and exports.[/expand]
4 (a) State five differences between a deposit account and a current account.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- With Current Account depositors use a cheque book to make withdrawal. However, with deposit account, the depositors use a passbook to make withdrawal.
- Deposit account holders receive interest on the funds they deposit. On the other hand, current account holder pay service charge to the bank.
- While a current account holder can withdraw from his account as many times as he pleases, a deposit account holder has a limited time/period to make withdrawal.
- A deposit account holder has to go personally to the bank to withdraw money. A current account holder can either go personally or issue a cheque for payment to be effected to any body.
- Whiles a current account holder can enjoy overdraft facility, a deposit account holder is not qualified to enjoy that facility.[/expand]
4 (b) Outline the processes involved in opening a current account.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- A person who intends to open a current account must show an introductory letter signed by an employer or guarantor who is either a customer of the bank or known by the bank.
- He then fills in a current account form. Some of the information he is required to provide on the form include: his name, residential or business address, employer, type of occupation, date of birth, usual signature, telephone number, etc.
- The potential current account holder is required to add an initial deposit to the completed form.
- An approval is supposed to be given by an official of the bank.
- Finally. the applicant is then given a cheque booklet and a pay-in slip book.[/expand]
5. Mention and explain five obstacles to international trade.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
International trade which is the exchange of goods and services between and among countries is beset with many obstacles among which include:-
- Language barriers:- Different languages are spoken by different countries all over the world. It is very difficult for businessmen who speak different languages to communicate effectively and thus cannot do business with each other. It is also difficult for them to get an agent who can trade in both languages.
- The problem of operational currency:- Differences in currencies is another obstacle to international trade. It is not every currency which is accepted in international trade. Thus if for instance Ghana wants to do business with U. K. (Britain) or America, she must first convert the cedis into pound sterling or dollars.
- Trade regulations:- Trade regulations also hinder international trade. Such regulations include artificial barriers such as tariffs, quotas, prohibitions, etc. hinder international business. These measures sometimes frustrate exporters and importers and thus discourage them from increasing their trading activities.
- The Financial problems:- Exporters and importers lack financial assistance. Hence they cannot conduct effective market research to find the most suitable markets. Lack of adequate market information about foreign country could lead to failure in business.
- Cultural Factors:- The existence of different cultural practices creates a problem in international trade. Culture which is the way of life of people in a particular locality can affect the demand for a product. Their beliefs, likes and tastes determine the demand for a foreign product. It also makes advertising and distribution of foreign products difficult.
- Different political and legal systems:- The political atmosphere goes to a larger extent to determine the extensity of international trade. Where the political system is stable, many investors come in to invest. But where the system is unstable, less foreign investment is undertaken. Besides that, the legal system affects it in the sense that if the system is favourably exposed to the trade, it flourishes and vice versa.[/expand]
6 (a) List and explain four remedies available to an injured party when there is a breach of contract.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
An injured party has the following remedies available to him when there is a breach of contract.
- Refusal of further performance: – If the breach is of a main condition the injured party may treat the contract as rescinded and refuse further performance. By treating the contract as rescinded, he makes himself liable to restore any benefits he has received.
- Sue on quantum meriut: – Under quantum meriut instead of the injured party suing for damages, he may claim payment for what he has done under the contract.
- Specific performance:- This is the actual performance of the contractual obligations as agreed upon by both parties. This is a court order. Instead of or in addition to rewarding damages to the injured party, the court will order the defaulting party to perform his or her part of the contract as promised.
- Injunction: – The injured party can apply to the court for an injunction order against the defaulting party. It is an order of the court restraining a person from doing some act. It is granted to prevent negative acts in a contract.
- The injured party can sue for damages: – Damages recognises that the injured party has had a legal right infringed upon. Damages are a form of compensation. It enables the injured party to be placed in the same financial position as if the contract has been performed.[/expand]
6 (b) Identify and discuss any three duties of an agent to the principal.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Non-delegation: – The agent must perform the work or duties personally. He has no right to delegate his duties to a sub-agent without the authority of his principal.
- Secret profits: – The agent must not make any secret profit out of the performance of his duties as an agent or beyond the commission or the remuneration paid by his principal.
- Duty to account: – The agent must pay to his principal all monies received. He is required to keep proper accounts and to produce them on demand.
- Conflict of interest:- The agent must not allow his own interest to conflict with his obligations to his principal.
- Due Diligence: – Generally the agent must exercise due diligence in the performance of his duties and to apply any special skill which he professes to have.[/expand]
7 (a) Briefly explain the influence the following have on business in your country:
- Labour Unions
- Consumers
- Investors
- Government
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Labour unions have collective bargaining power which they use in the negotiation of wages and salaries as well as other conditions of work or service that have much influence on business. They also have strike action, work to rule, picketing, boycott etc. that have much influence on business operations in a country.
- Consumers are the lifeblood of every business and have much influence on their operations in that the interest of consumers of a product is supreme in modern business. The consumer dictates the quality, quantity, price and place decision of the product because his likes and dislikes are normally considered.
- Investors provide capital to the business because they want to have a share in its yearly profits. They influence the operations of the business with respect to resource allocation and utilization.
- Government formulates the laws that regulate the operation of businesses in every country. It therefore provides the social, political and economic environment in which business organizations operate. It also provides infrastructure like roads, water, electricity etc. to facilitate business operations.[/expand]
7 (b) Mention and explain two functions performed by computers in business.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Processing of data:- This involves the processing of raw data into useful form.
- Storing of data and information:- The computer also stores data through the use of electronic media such as main memory on the computer.
- Retrieval of information:- Through this function, data stored in the computer can be retrieved when needed.[/expand]
WASSCE Past Questions and Answers – Business Management 1993 – Paper 2
CASE STUDY
Read the following case carefully and answer the questions which follow:[expand title=””]
ALUPSON LIMITED
Mr. Abugri sought and found an administrative position in Alupson Ltd. He started well as a successful manager. He had a good graduate training in two professions including business administration. He also acquired good problem solving skills.
From the beginning of his career in Alupson Ltd., he defined the organizational structure and displayed the chart in every office. He thus found a cure to the problem of authority-responsibility relationship and span of control. Next in his re-organization, Mr. Abugri introduced a system of assessing the contribution and effectiveness of the employees to the organization. Factors such as knowledge of work, work habits, devotion to duty, reliability, cost consciousness and a lot more, were rated annually. The practice enhanced management decision on many issues. Mr. Abugri was also known to have a sense of humour which softened the view many people had that managers of the company were bossy.
Mr. Abugri seemed self-sufficient and created the impression that he did not need any supervisor’s advice in handling administrative problems. There was little room in his plans for the ideas of others. He always had a view of his own. His desire to solve problems made him carry too much on his shoulders. In order not to take the blame for his subordinates’ inefficiencies, he often ran away from delegation.
Mr. Abugri showed a willingness to solve the most difficult problems himself. Many felt he rushed into situations that required considerable fore thought and caution if they were to be handled well. Even though his position was high, he was not to act on his own as he often did, for there were three men above him who exercised general control and direction of all the activities of the Company.
Mr. Abugri had one nickname “What-did-he-say”. Every junior office called him by this name after their weekly meetings. The minutes of one of their meetings read:
“I have called you together to elucidate on our dire economic situation. We are in competition with tigers that are snapping at our feet. If our company is to survive, we must all pitch and pull together. Next, we have to beef up our sales force. Customers are the lifeblood of our business and although they are not always right, they must still be handled with tender gloves”.
The meeting lasted for forty minutes. All one could hear after the meeting was the singing of Mr. Abugri’s nickname, “What-did-he-say”.
[/expand]
1(a) Explain briefly three factors that accounted for the success of Mr. Abugri in his early administrative career.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
The following factors accounted for Mr. Abugri’s administrative career in the early stages.
- He adopted a system by which he could assess the contribution and effectiveness of his employees. With this system in place, (i.e. employee appraisal system) Mr. Abugri could locate employees who were performing below expectation. This practice enhanced the management decision making process in terms of personnel recruitment, remuneration, motivation, etc.
- The interpersonal relations he exhibited at the early stage of his career contributed immensely to his early success. -He was not bossy. In effect good and conducive working relationship developed among the workers.
- He put in place a well-defined organizational structure, which solved the problem of authority responsibility relations and the span of control problems. This also enabled reporting systems to be clear in the minds of the workers. This means that they all get to know their authority – responsibility scope, limits and how each individual is related to the other.
- He also had the right education and training for the job (i.e. graduate education and training in administration).[/expand]
1 (b) What do you detect as the weaknesses of Mr. Abugri as an administrator.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Mr. Abugri lacked the ability and willingness to delegate authority to his subordinates. This led to too many workloads on him.
- He had a problem with effective communication.
- He had no respect for top Executive Officers. He did not consult them on certain issues that required their attention. He hastened in taking important decisions.
- He was autocratic and did not allow the active involvement of others in decision making process.
- He did not have respect for the opinions and views of others. He did not seek advice from others.[/expand]
1 (c) Write three recommendations, which in your opinion will help, correct Mr. Abugri’s Shortcomings.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Mr. Abugri must try and improve upon his communication skills. He should learn to use simple language so that his subordinates can understand him.
- He must also cultivate the habit of consulting higher authorities whenever the need arises on certain vital if not crucial decision making process.
- He must also learn to delegate authority to low level workers so as to have time to attend to sensitive and important assignments.[/expand]
2. Controlling is an important management function. Explain briefly four steps that a manager will take to control the work of factory employees.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
Control may be defined as the process through which managers ensure that actual activities conform to planned activities. It is the process of monitoring performance to ensure that it conforms to predetermined standards.
- The first of the four steps that a manager will take to control the work of factory employees is to establish standards of performance. This involves deciding in advance what is to be done in conformity with set objectives and specifications.
- The second step is that the manager should measure performance against expected standards. That is actual work done by the employees should be measured against expected standards.
- The third step involves making comparison of actual results against expected standards. Here measured results are compared with the established standards to assess the degree of deviation or conformity.
- The fourth step is where the manager takes corrective action. When performance falls short of standards, corrective action should be taken to put things right. This corrective action may involve making some changes in the organisation’s operations.[/expand]
3. The personnel manager of Food Luck Company Ltd. wants to employ five competent secretaries. Outline and explain the selection procedures you would expect him to follow.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
The following procedures may be taken in the selection of the secretaries:
- Advertisement in the Dailies/Notices on the company’s notice boards:-Advertisement in the Daily newspapers, magazines, journals, radio and television should take the form of job description and job specification. Job description states the title and location of the job, the main function, responsibility, limits of authority, physical working conditions etc. It typically portrays job content. Job specification, on the other hand, describes the knowledge, skills and experience, educational levels required to carry out the job. It therefore describes the physical qualities and characteristics needed to perform the job.
- Collection of application forms and letters:- All the application forms and letters from prospective job applicants must be collected and recorded.
- Short-listing of applicants:- Since all types of applications are received when jobs are advertised, it is necessary to short-list the applicants. Short-listing also referred to as the screening stage involves the sorting out or elimination of those applicants judged unqualified for the job. It is normally done by matching the applications against the employer’s requirements. Those short-listed based on their merit are invited for interview.
- Interview:- All short-listed applicants should be interviewed by the personnel manager. Interview involves a quick evaluation of the applicant’s suitability for the job. It gives the organization an opportunity to assess the applicant directly; and it gives the applicant an opportunity to learn more about the organization. Note here that all documents tendered will be inspected and evaluated.
- Practical Test:- Selection tests are used to supplement other techniques. A short written test and practical test should be conducted by the personnel manager to test their typewriting and shorthand skills.
- Background Investigation:- This is carried out in order to confirm information supplied by applicants on their application forms. It is used to check the truthfulness of a candidate’s application form. Further information about the applicant may be sought from one or more of the candidates’ referees, previous employers and schools.
- Medical test or examination:- Medical examination is carried out to determine the physical fitness of the applicants and whether they have any hidden or contagious diseases. Candidates with contagious diseases will be rejected.
- Job offer:- If the candidate successfully passes through all the stages and continues to express interest for employment, a job offer may be made. Appointment letters may be given to successful candidates.[/expand]
4. Briefly explain what the following terms mean
- Trade Credit
- Bank Overdraft
- Hire Purchase
- Lease
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Trade Credit: This is one of the main sources of finance for business organizations. This involves the purchase of goods or services that is backed by a promise to pay at a future date. It gives the debtor the opportunity to sell the goods or services, make some profit before paying for them. It however depends on the credit worthiness of the debtor.
- Bank Overdraft: Bank Overdraft is a short-term source of business finance. It is a credit facility granted by banks to their customer. Here, a customer is allowed to overdraw up to a certain limit on application to his bankers. Interest is charged only on the actual amount overdrawn and it attracts a short period of repayment.
- Hire Purchase: This is an important source of finance for businessmen who cannot make full payment for items purchased. Under the hire purchase agreement, the businessman undertakes to pay for items purchased in instalments after an initial deposit has been paid. The instalment payments are made regularly, may be monthly or weekly until the total purchase price is paid. The buyer however takes complete possession of the goods after the last instalment has been paid.
- Lease: This is a legal agreement where organizations lease out their fixed assets which are lying idle to individuals and organizations at a fee. The fee could be a source of finance for business organizations.[/expand]
5. State and explain six functions performed by retailers in the buying and selling of goods and services.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
Retailers perform the following functions
- Breaking bulk: – retailers buy in bulk from wholesalers. Afterward, they break it down into small quantities and sell them to consumers.
- Collecting information from the customer to the manufacturer. The retailer provides the manufacturer with the necessary market information they gather through their interactions with consumers. The manufacturer can rely on this information to make improvement in the quality of his products or services.
- Also, retailers make products affordable to the final consumers by dividing them ito smaller quatities and prices for the consumers to buy.
- Retailers offer education to the final consumers about the usage of the products.
- They help to promote the product to the consumer by informing the consumer about some unique attributes of the product.
- Retailers repack, measure, weigh and standardise products in convenient parks for sale to final consumers.
- They help to provide further storage space for the product. Retailers also buy and store goods from wholesalers.[/expand]
6 (a) What is collective bargaining?
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
Collective bargaining can be defined as a process through which representatives of employees and those of employers come together to negotiate matters relating to employment. It is a process by which representatives of employers and those of employees meet to bargain over and agree upon significant terms of employment. These terms may cover areas such as: workers’ incomes, job security, working conditions, hours of work, procedure by which disputes should be settled etc. During such meetings, efforts are made to reach a consensus.[/expand]
6 (b) State and discuss five advantages of Collective Bargaining.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Collective bargaining exhibits some form of industrial democracy. This is because through it management and labour are able to argue, deliberate, persuade and influence each other. This ensures that they arrive at a consensus on matters relating to working conditions and productivity. Thus it brings about a feeling of participation in decision-making.
- It also serves as communication process, which helps each side to understand the other’s view points. This helps in developing good relationship between employers and employees.
- Through collective bargaining, targets and objectives are more realistically set. With all other things being equal, high productivity can be achieved.
- Collective bargaining process provides the machinery through which all conflicts are resolved. It projects a platform on which all differences are settled.
- It also reduces labour turnover and thus enhances job security.[/expand]
7 (a) Four Senior Secondary School graduates wish to team up to operate a carpentry business. Mention and Explain three possible types of business units that they can form.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
The three types of business units that they can form are:-
- Partnership:- this is a form of business organization in which two or more people contribute to do business with a view to making profit. The membership of a partnership firm may range from two to twenty.
- A Co-operative Society:- This is a type of business ownership in which a group of people with common interest come together and contribute capital to undertake production or distribution of goods with the aim of maintaining the welfare of its members. Members act as both owners and customers.
- A private limited liability company:- This is a type of company run by a small group of people mostly friends or family members. They mostly have at least two members and a maximum of fifty members. Each member contributes shares towards initial capital.[/expand]
7 (b) Mention and explain three sources of finance available to them to raise capital.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Personal Savings:- This refers to contributions from the individual members in the form of cash or materials.
- Trade Credit:- This involves the purchase of goods that is backed by a promise to pay at a future date. It gives the debtor the opportunity to sell the goods, make some profit before paying for them. It however depends on the credit worthiness of the debtor.
- Hire Purchase:- Under the hire purchase agreement, the business man undertakes to pay for items purchased in instalments after an initial deposit has been paid.
- Leasing:- Here organizations lease out fixed assets (e.g piece of land, building, machinery, equipment, etc.) which are lying idle and would not be used immediately at a fee.
- Loans from Banks, friends, relatives and other financial institutions.
- Donations from friends and relatives.[/expand]
8. Explain six advantages that a manufacturer may derive from promoting his goods.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Promotion informs: – That is it creates awareness about the availability of a product on the market and arouses the interest of the consumer. It also informs the consumer about the new uses of a product and its desirable qualities.
- Promotion persuades – promotion persuades both existing and potential customers to purchase that particular product in preference to all others.
- Promotion reminds: – It serves as a reminder to consumers that the product is still available in the market.
- Promotion also educates the consumer about the effective use of the product.
- Promotion helps to boost the sales of a particular product or service.
- Promotion projects the image of the business
- Promotion increases market share.
- Promotion stimulates product usage and patronage.[/expand]
9(a) What is Directing?
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
Directing is a management process that deals with communication, motivation, supervision, leading, guidance and discipline of workers in order to achieve a desired result. Directing as a management function therefore, seeks to guide, motivate, stimulate and lead subordinates towards the accomplishment of organisational objectives.[/expand]
9. (b) State and explain five things that a manager may do to raise the morale of his/her subordinates.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
A manager may boost the morale of his/her subordinates by:
- Providing them with adequate reward system. The reward system must be fairly and equitably distributed. It must also comply favourably with what their colleagues obtain elsewhere as well as their output levels.
- Providing them with opportunity for training and development. Training and development geared towards equipping subordinates with the right skills, attitudes and knowledge will also raise their morale.
- Giving them gives recognition and praise when it is due.
- Establishing or instituting open communication channels. This will allow subordinates to feel free to approach their superiors when necessary. This eliminates suspicion and mistrust and creates a bond of trust and confidence among employees.
- Delegating authority to subordinates to perform specific assignments on his behalf.
- By promotion, which involves raising a person to a higher status in the organisation. This is because, promotion gives recognition for good performance and the readiness to assume greater responsibility.
- Showing fairness, firmness and inspiring subordinates to work with confidence.[/expand]
10. Every product passes through a life cycle with the help of a diagram, explain the various stages through which a typical manufactured product passes in its life cycle for each stage, identify a typical marketing strategy that must be adopted.
Suggested Answer:[expand title=””]
- Introduction Stage: – This stage starts when the new product is first introduced into the market. The company incurs high cost of production, profits are also negative or low because of the low sales and high distribution and promotion on expenses. Promotion spending is high to inform consumers about the new product and get them to try it. The marketing strategy here is that, promotion must be more informative, persuasive and educative. With regards to pricing, the marketer may decide to adopt the skimming pricing or penetration pricing. The pricing method to adopt depends on the distinctiveness of the product.
- Growth Stage: – At this stage, sales will start climbing quickly. It usually brings gradual reduction in cost, and an increase in sales and profit returns. Competition usually starts to set into the market.The firm uses several strategies to sustain rapid market growth and these includes improving product quality, enter new market segments, enter new distribution channels, shift advertising from building product awareness to building product conviction and purchase.
- Maturity stage: – There is keen competition at this stage as many competitors have entered the market. Profits decline as promotion costs climb. Competitors begin to cut prices to attract business. The marketing manager should consider modifying the product, market and marketing mix.
- Decline Stage: – Here sales may plunge into zero or they may drop to a low level and continue there for some time. The product may die out of the market. Many customers leave the market and products with strong.
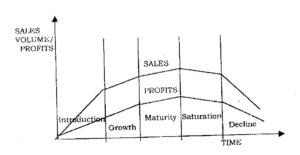
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE[/expand]
You Might As Well Have Interest In The Following:
- Business Management 2019 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 2007 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 2006 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 2005 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 2004 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 2003 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 2002 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 2001 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 2000 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 1999 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 1998 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 1997 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 1996 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 1995 Past Questions and Answers
- Business Management 1993 Past Questions and Answers
Conclusion:
I believe Educareguide has been of help to you with regards to your subject of concern. Also there are many other contents we have available to help you in your education.
Furthermore, if there is any contribution/comment/concern that you would want to make, it is warmly welcome on our site. Simply proceed to Login/Register to submit your post.
Now, please, subscribe to Educareguide and contact us for further assistance for your education. Finally, fill the contact form on the side bar to reach us.
Nevertheless, do not forget to pass a comment in the comment section below. Indeed, we will gladly appreciate to know how you think about this article. Thanks.